FM fluorescent dyes for imaging of cell membrane and tracing neuronal cells
The FM fluorescent dye series currently consists of five dyes, including FM 1-43、FM 2-10、FM 4-64、FM 5-95, etc. These dyes belong to a class of lipophilic styrene fluorescent dyes, which are currently employed for the specific labelling of cell membranes of living cells, tracer imaging of neuron cells, and tracking of vesicles such as endocytosis, exocytosis and other vesicle-related cellular processes[1-13].
- ●Non-toxic to cells and can be used for staining and labelling of living cells.
- ●Excellent water solubility and are non-fluorescent in aqueous solution, but emit bright fluorescence when they bind to cell membranes and analogous membrane structures.
- ●Covers the red colour region to the near-infrared I region (600 - 800 nm).
- ●In comparison with other cell membrane dyes, they exhibit several advantageous properties, including high specificity, uniform staining, and bright signals.
These dyes find extensive application in the labelling of membrane structures of living cells, with a particular emphasis on the staining of plant cell membranes. These dyes permit highly specific imaging of membrane structures in plant cells, including high-definition imaging of cell membranes in root tip cells, leaf epidermal cells, and other plant cells such as those found in onions, tobacco, rice, and A. thaliana.
Furthermore, these dyes can be utilised for the labelling of the plasma membrane of animal cells, as well as for the tracking and labelling of neuronal cells by fluorescent signals. In neurons that are actively releasing neurotransmitters, the dyes are internalised in recyclable protruding vesicles, resulting in the neuronal cell ends being brightly dyed. This property renders them suitable for the study of neuron-related physiological processes.
For instance, FM 1-43 and FM 4-64 can be used for highly specific imaging of membrane structure of plant cells, including HD imaging of cell membranes of onion (FIG. 1-2), tobacco (FIG. 3-4), rice, Arabidopsis and other plants, such as root tip cells and leaf epidermis cells.
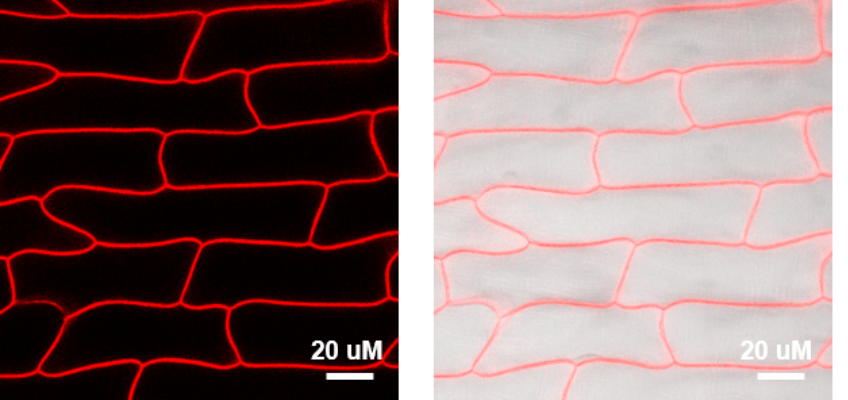
Fig. 1. Confocal laser imaging of onion epidermal cells stained with FM 1-43
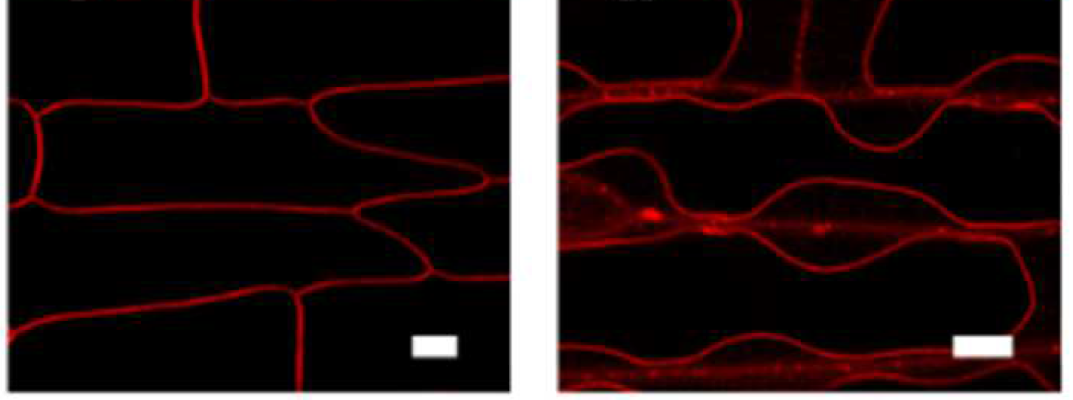
Fig. 2. Confocal laser imaging before and after separation of onion epidermal cytoplasmic wall stained by FM 4-64
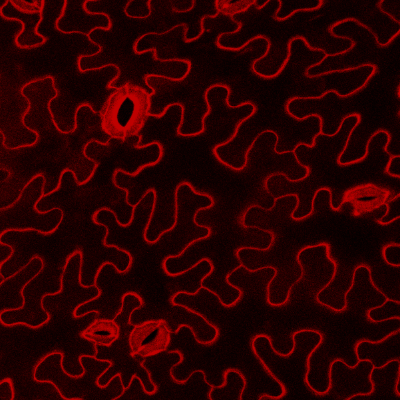
Fig. 3. Confocal laser imaging of epidermal cells and guard cells of tobacco leaves stained with FM 1-43
Fig. 4. Confocal laser photograph of tobacco root tip cells stained with FM1-43

产品列表
| 品名 | CAS | 货号 |
|---|---|---|
| FM 1-43 Dye, 95% FM 1-43 荧光染料 | 149838-22-2 | 208840 |
| FM 2-10 Dye, 95% FM 2-10 荧光染料 | 336185-20-7 | 594679 |
| FM 5-95 Dye, 90% FM 5-95 荧光染料 | 872979-87-8 | 2327685 |
| FM 4-64 Dye, 90% FM 4-64 荧光染料 | 162112-35-8 | 623467 |
参考文献
- Betz. W.; Bewick, G. Science, 1992, 255, 200-203.
- Heuser, J.; Zhu, Q.; Clarke, M. J. Cell Biol., 1993, 121, 1311-1327.
- Vida, T. A.; Emr, S. D. J. Cell Biol., 1995, 128, 779-792.
- Whalley, T.; Terasaki, M.; Cho, M. S.; Vogel, S. S. J. Cell Biol., 1995, 131, 1183-1192.
- Murthy, V. N.; Stevens, C. F. Nature, 1998, 392, 497-501.
- Betz, W. J.; Angelson, J. K. Annu. Rev. Physiol., 1998, 60, 347-363.
- Sharp, M. D.; Pogliano, K. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1999, 96, 14553-14558.
- Wiederkehr, A.; Avaro, S.; Prescianotto-Baschong, C.; Haguenauer-Tsapis, R.; Riezman, H. J. Cell Biol., 2000, 149, 397-410.
- Bolte, S.; Talbot, C.; Boutte, Y.; Catrice, O.; Read, N. D.; Satiat-Jeunemaitre, B. J. Microsc., 2004, 214, 159-173.
- Rea, R.; Li, J.; Dharia, A.; Leitan, E. S.; Sterling, P.; Kramer, R. H. Neuron, 2004, 41, 755-766.
- Jennings, P.; Bertocchi, C.; Frick, M.; Haller, T.; Pfaller, W.; Dietl, P. Cell. Phys. Biochem., 2005, 15, 159-166.
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Chu, H.; Xiong, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Feng, H.; Zhu, E.; Zhou, J.; Huang, P.; Qian, Z. Anal. Chem., 2022, 94, 4048-4058.
- Zuo, J.;Zhu, E.; Yin, W.; Yao, C.; Liao, J.; Ping, X.; Zhu, Y.; Cai, X.; Rao, Y.; Feng, H.; Zhang, K.; Qian, Z. Chem. Sci., 2023, 14, 2139-2148.
推荐阅读
细胞结构及细胞器荧光染料高稳定性、高灵敏度荧光试剂
荧光染料选择指南
根据荧光性质选择荧光染料
根据应用选择荧光染料